Logistics management is a vital part of supply chain management. It involves planning, implementing, organizing, and controlling both the effective and efficient forwarding and reversal flow and storage of goods. Additionally, it gathers and processes important information that starts from the product’s point of origin to its point of consumption to meet the customer’s requirements. All these control functions ensure effective business management in working toward achieving the business’s planned objectives.
Logistics Controlling Helps with Complexity of Supply Chains
Logistics controlling in an ERP-integrated supply chain can become very complex process. This is because it applies to a broad area of activities. Consider the following example presented in Fig. 1 that illustrates the place of logistics controlling in a company’s controlling system that allows for the basic area of logistics controlling activities.
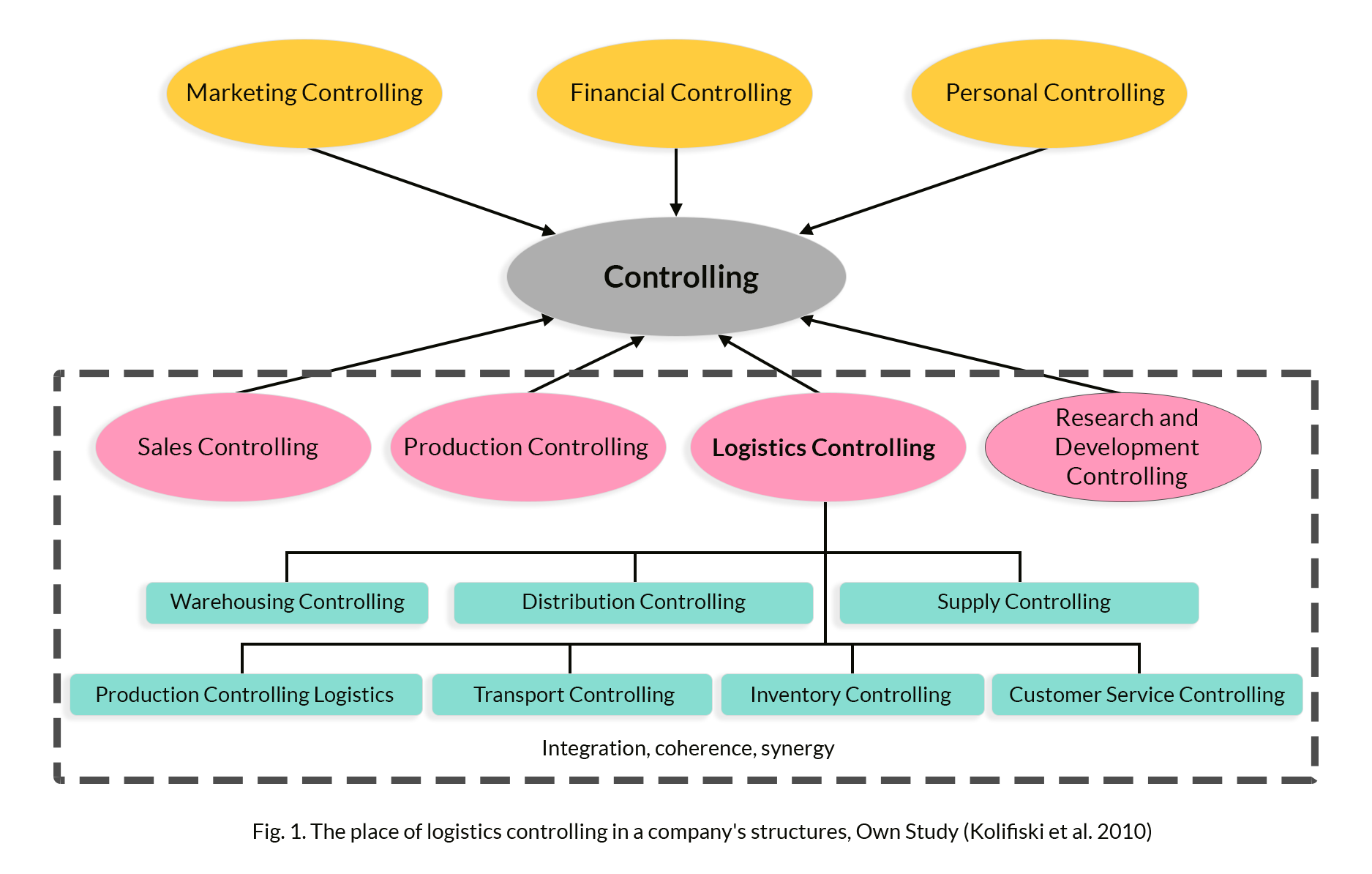
In this example, “Logistics Controlling” covers seven areas, including:
1. Warehouse Controlling
2. Distribution Controlling
3. Supply Controlling
4. Production Logistics Controlling
5. Transport Controlling
6. Inventory Controlling
7. Customer Service Controlling
The objectives of supply chain management activities, such as design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring intend to:
- Create net value
- Build a competitive infrastructure
- Leverage worldwide logistics
- Synchronize supply to demand
- Measure global performance
As an important tool in the supply chain, logistics controlling is now a real determinant with managing the aforementioned multi-subjective structures. Therefore, the range of controlling reaches far beyond the scope of any one company. With the complexity of the supply chain, logistics controlling integrates functions that are orientated on a specific product, and its technical processes and aspects involving social integrations.
By implementing controlling in an ERP-integrated supply chain, the risk is shared with minimizing the amount of engaged funds and applying a sustainable development doctrine. This is done by perfecting one’s qualifications with the help of their business partners’ qualifications.
Ecological Benefits of Logistics Controlling
The strong cooperation and information shared during each stage of implementing logistics controlling creates value and assists with generating long-term profits that are competitive for both the entire supply chain and the environment. The following figures shows the ecological benefits that can be achieved through logistics controlling.
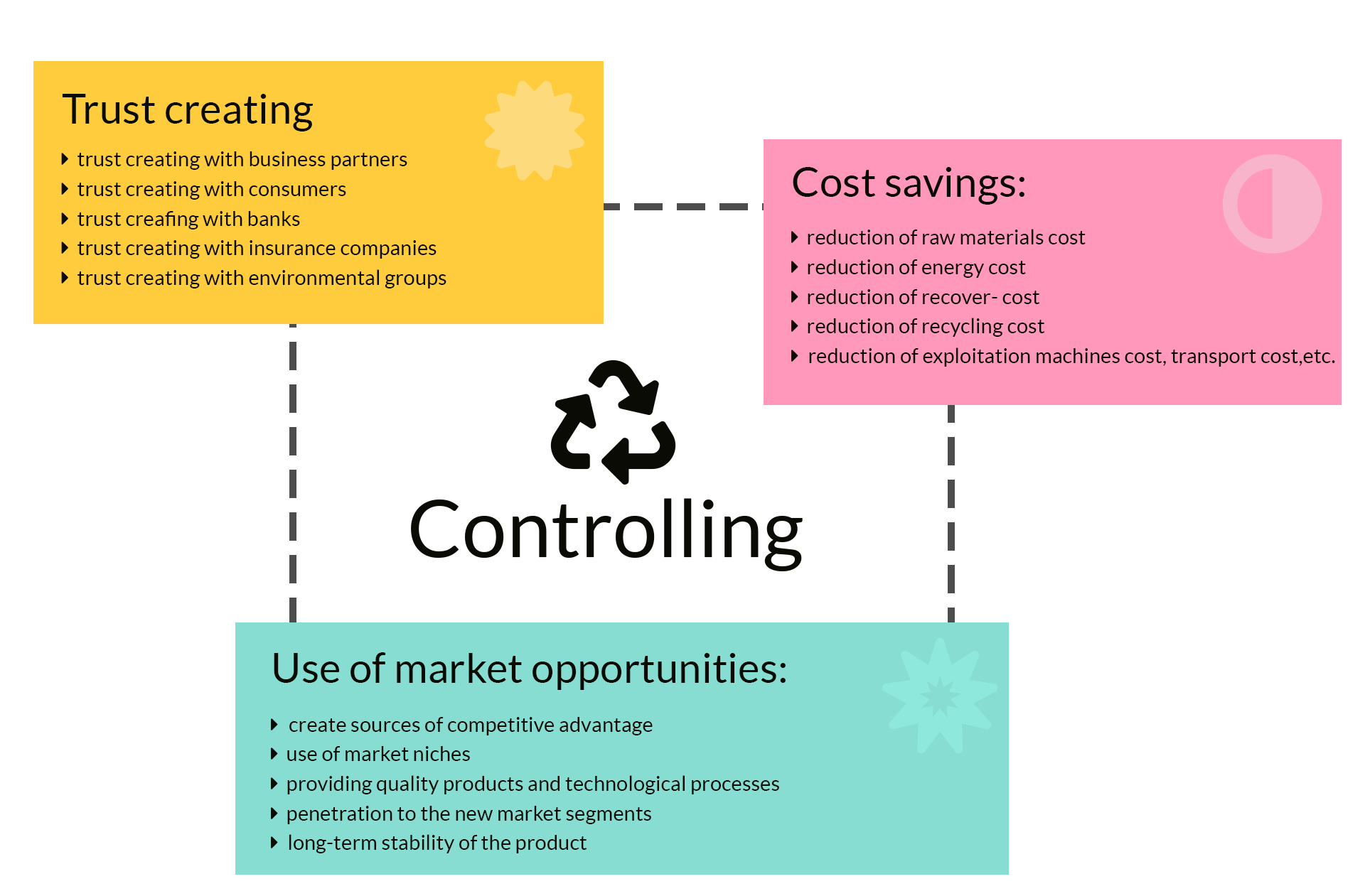
Logistics controlling involves trust creating, cost savings, and use of market opportunities. Generally, the logistic supply chain is based on efficient distribution to guarantee the physical flow of goods, in addition to the information connected to the transfer. However, the flow of information coming from multiple links in supply chains can create multiple problems that can disrupt supply chains. The effectiveness of information management is central and vital to successfully executing the responsibilities and processes of logistics and supply chain. Logistics controlling expands the efficient information infrastructure in ERP-integrated supply chains and exchanges data about the flow of goods based on three principles:
1. Unifying data that is exchanged in a supply chain
2. Improving technical-organizational possibilities of information exchange between the various partners involved in a supply chain
3. Guaranteeing that the data exchanged is lawfully binding
References and Further Reading
- "ERP Integration as a Support for Logistics Controlling in Supply Chain (2011)" , by Adam Koliński and Paweł Fajfer